
Understanding how to calculate cost of goods manufactured is essential. It allows you to analyze production expenses and make informed decisions. Whether you’re dealing with materials or finished products, accurate calculations provide clarity on where your money is going. This guide simplifies the process, helping you streamline operations and boost profitability.
Key Takeaways
Knowing the Cost of Goods Manufactured (COGM) helps manage production costs and boost profits.
COGM includes materials, worker pay, and factory expenses needed to find total production costs.
Counting work-in-progress (WIP) inventory ensures only finished goods are included for better financial records.
Tools like ERP software make COGM calculations easier, saving time and avoiding mistakes.
Checking COGM often can show ways to save money and make the business run better.
What Is the Cost of Goods Manufactured (COGM)?

Knowing the cost of goods manufactured (COGM) is very important. It shows how well your business controls costs and produces goods. Let’s explain it simply.
Definition and Purpose of COGM
COGM includes all direct costs for making products in a set time. These costs are things like raw materials, worker wages, and factory expenses. It does not include indirect costs like advertising or office expenses.
Why is this important? COGM shows how much it costs to make your products. It helps you see where your money goes and if your prices cover costs and leave profit. Watching COGM over time can show where to save money or work better.
Here’s why COGM matters:
It shows how much it costs to make your products.
It helps you price products to stay competitive and earn profit.
It tracks the value of finished goods for better inventory control.
It lets you compare your performance over time or with others.
Key Components of COGM
COGM is made up of smaller parts, not just one number. These parts are:
Direct Materials: The raw items used to make products.
Direct Labor: The pay for workers making the products.
Manufacturing Overhead: Costs like electricity, repairs, and factory rent.
To find COGM, you also need to check unfinished goods. This means looking at their value at the start and end of the period.
Here’s an example to show the parts:
Component | Value |
|---|---|
Opening Inventory | 3000 packets |
Closing Inventory | 1000 packets |
Freight In | $20,000 |
Discounts Received | $4,500 |
Purchase Costs | $50,000 |
Cost of Opening Inventory | $6,000 |
Cost of Closing Inventory | $2,000 |
Total COGS | $69,500 |
Why COGM Matters for Businesses, Including Building Materials
For businesses, especially in building materials, COGM is key. It helps control costs so you don’t overspend on materials or labor. It also helps manage inventory, avoiding too much or too little stock.
Check this chart to see how COGM affects your business:
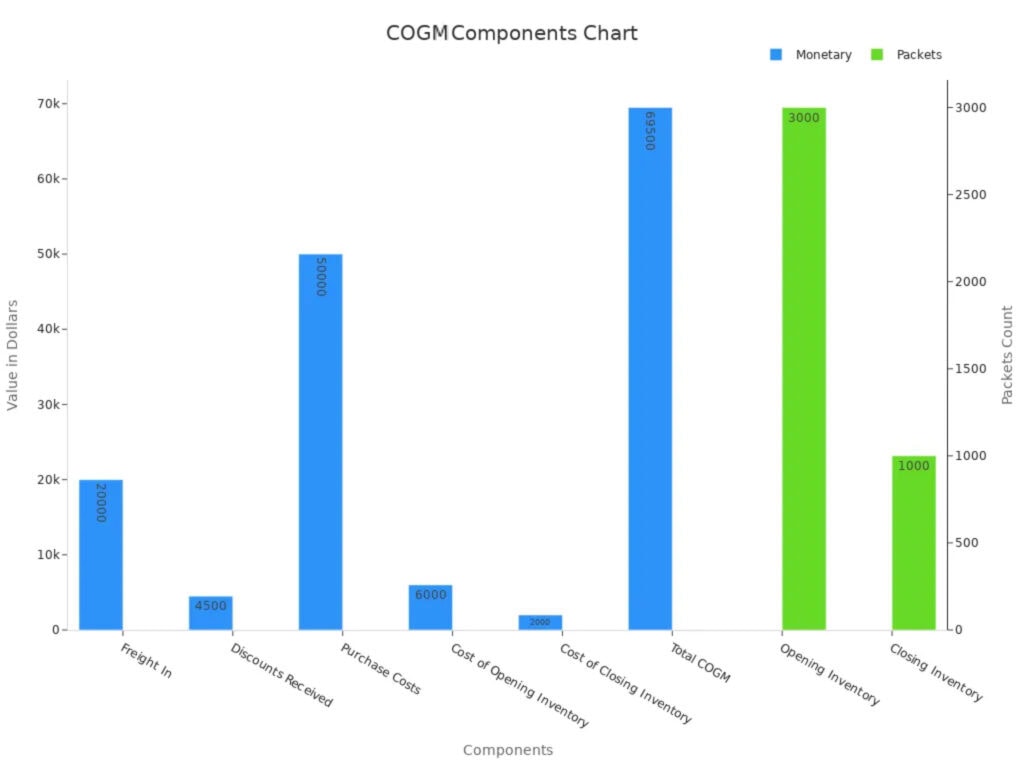
Here’s why it’s important:
Cost Control: Find rising costs early and fix them.
Inventory Management: Keep the right amount of stock.
Performance Evaluation: Check how well production works and improve it.
Pricing: Set prices that are fair and profitable.
Financial Reporting: Make accurate budgets and financial reports.
For building materials businesses, where profits can be small, knowing COGM helps you stay competitive and make money.
The Formula to Calculate Cost of Goods Manufactured
Knowing how to calculate the cost of goods manufactured (COGM) is important. It helps you manage production costs and improve efficiency. The formula is simple once you understand it.
Breaking Down the COGM Formula
The formula adds up production costs and adjusts for unfinished goods. Here’s the formula:
COGM = Total Manufacturing Costs + Beginning WIP Inventory – Ending WIP Inventory
Let’s explain it step by step:
Total Manufacturing Costs include materials, labor, and overhead.
Beginning WIP Inventory is the value of unfinished goods at the start.
Ending WIP Inventory is the value of unfinished goods at the end.
Using this formula, you can find out your production costs. For example, if total manufacturing costs are $100,000, beginning WIP inventory is $10,000, and ending WIP inventory is $5,000, then:
COGM = $100,000 + $10,000 - $5,000
COGM = $105,000
This shows the total cost of finished goods for the period.
Main Parts: Materials, Labor, and Overhead
To calculate COGM, you need to know its three main parts:
Direct Materials: These are the raw items used to make products. For example, wood and screws for cabinets.
Direct Labor: This is the pay for workers making the products, like carpenters.
Manufacturing Overhead: These are extra costs like electricity, rent, and repairs.
Here’s how to calculate total manufacturing costs:
Add up the cost of materials used.
Include wages for workers directly making the product.
Add overhead costs like utilities and equipment upkeep.
For example, if materials cost $50,000, labor costs $30,000, and overhead is $20,000:
Total Manufacturing Costs = $50,000 + $30,000 + $20,000
Total Manufacturing Costs = $100,000
This total is the base for finding COGM.
Adjusting for Unfinished Goods
Unfinished goods, or work-in-progress (WIP), are partly made products. To calculate COGM, you must adjust for these.
Here’s how:
Start with the value of beginning WIP inventory.
Add total manufacturing costs.
Subtract the value of ending WIP inventory.
This ensures you only count fully finished goods.
Here’s an example of how adjusting for WIP can help businesses:
Case Study | Less Downtime | More Output | Cost Savings | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
National Oilwell Varco (NOV) | 20% | N/A | N/A | N/A |
Chemical Plant | 13% | N/A | 20% | N/A |
Healthcare Services | 17% | N/A | 22% | $4.5 million |
These examples show how tracking WIP can save money and improve production. By using the formula, you can find ways to work better and save costs.
Step-by-Step Instructions to Calculate COGM

Knowing how to calculate COGM helps you understand production costs. It also improves how efficiently your business runs. Follow these simple steps.
Step 1: Find Total Direct Materials Used
Start by figuring out the cost of raw materials. These are the basic items needed to make your products, like wood or steel. To calculate this:
Add the cost of raw materials you bought.
Include freight-in costs (shipping materials to your factory).
Adjust for inventory changes:
Add the value of starting inventory.
Subtract the value of ending inventory.
Use this formula:
Total Direct Materials Used = Raw Materials Purchased + Freight-In + Beginning Inventory - Ending Inventory
For example, if you bought $50,000 in materials, spent $5,000 on shipping, and your inventory changed from $10,000 to $8,000:
Total Direct Materials Used = $50,000 + $5,000 + $10,000 - $8,000
Total Direct Materials Used = $57,000
💡 Tip: Tools like pricing data from suppliers can help estimate costs for 2025.
Step 2: Add Direct Labor Costs
Next, include the pay for workers who make your products. This includes wages, benefits, and overtime for people directly involved in production. For example, carpenters building cabinets.
To calculate labor costs:
Multiply hours worked by the hourly pay rate.
Add extra costs like benefits or overtime.
If workers worked 2,000 hours at $20 per hour and earned $5,000 in benefits:
Direct Labor Costs = (2,000 hours × $20/hour) + $5,000
Direct Labor Costs = $40,000 + $5,000
Direct Labor Costs = $45,000
💡 Note: Tracking labor costs helps find ways to work better.
Step 3: Add Manufacturing Overhead
Finally, include manufacturing overhead. These are indirect costs like rent, utilities, and equipment repairs. They support production but don’t directly make the product.
To calculate overhead:
List all indirect costs for production.
Divide these costs among products using a fair method, like machine hours.
For example, if rent is $10,000, utilities are $5,000, and equipment repairs are $3,000:
Manufacturing Overhead = $10,000 + $5,000 + $3,000
Manufacturing Overhead = $18,000
💡 Pro Tip: Assign overhead costs carefully. Use methods like machine usage to split costs fairly.
Once you finish these steps, combine everything using the COGM formula:
COGM = Total Direct Materials Used + Direct Labor Costs + Manufacturing Overhead
This process ensures you count every cost correctly. It helps you set prices, plan budgets, and control spending.
Step 4: Adjust for Beginning and Ending WIP Inventory
Changing for work-in-progress (WIP) inventory is very important. WIP inventory means items partly made but not ready to sell. To calculate correctly, you must include the value of WIP at the start and end of the time period.
Here’s how to do it:
Start with Beginning WIP Inventory: This is the value of unfinished goods at the start.
Add Total Manufacturing Costs: Add up costs for materials, labor, and overhead.
Subtract Ending WIP Inventory: This is the value of unfinished goods at the end.
This step makes sure only finished goods are counted in your COGM. For example, if your beginning WIP is $3,000, total manufacturing costs are $50,000, and ending WIP is $5,000, the calculation is:
Adjusted COGM = $50,000 + $3,000 - $5,000
Adjusted COGM = $48,000
Why is this adjustment important?
Adjusting WIP inventory ensures accurate cost tracking. It shows the real production costs and avoids mistakes in financial reports. This helps you make smarter business choices.
Step 5: Finalize the Calculation with an Example
After adjusting WIP inventory, finish the COGM calculation. Let’s use an example to explain.
Here are the details:
Raw Materials: $20,000
Direct Labor: $10,000
Factory Overheads: $4,000
Beginning WIP Inventory: $3,000
Ending WIP Inventory: $3,000
Use the formula:
COGM = Total Manufacturing Costs + Beginning WIP Inventory - Ending WIP Inventory
First, find total manufacturing costs:
Total Manufacturing Costs = Raw Materials + Direct Labor + Factory Overheads
Total Manufacturing Costs = $20,000 + $10,000 + $4,000
Total Manufacturing Costs = $34,000
Next, adjust for WIP inventory:
COGM = $34,000 + $3,000 - $3,000
COGM = $34,000
The total cost of goods manufactured is $34,000. This is the cost of all finished goods for the period.
Here’s a simple table for better understanding:
Cost Component | Amount ($) |
|---|---|
Raw Materials | 20,000 |
Direct Labor | 10,000 |
Factory Overheads | 4,000 |
Beginning WIP Inventory | 3,000 |
Ending WIP Inventory | 3,000 |
Total Cost of Goods Manufactured | 34,000 |
Pro Tip: Review your COGM often. It helps you find problems and save money. This improves your production and profits.
COGM vs. Related Concepts

Difference Between COGM and Total Manufacturing Costs
You might ask how COGM differs from total manufacturing costs. They are connected but have different uses. Total manufacturing costs include all production expenses like materials, labor, and overhead. COGM adjusts these costs by considering changes in work-in-progress (WIP) inventory. This adjustment focuses only on finished goods’ costs.
Here’s a simple comparison:
Term | Description |
|---|---|
Total Manufacturing Costs | All production costs in a period |
COGM | Adjusts TMC for WIP inventory changes to show finished goods’ cost |
COGS | Adjusts COGM for finished goods inventory changes to show sold goods’ cost |
Knowing this difference helps track production costs better. For example, if WIP inventory grows, COGM will be lower than total manufacturing costs. This can help you manage inventory and improve efficiency.
How COGM Relates to Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
COGM and COGS are linked but not the same. COGM shows production costs for finished goods. COGS shows the cost of goods sold during a time period. In manufacturing, production costs start as WIP inventory. When goods are sold, these costs become COGS on your income statement.
Think of it like this: COGM shows what it costs to make goods. COGS shows the cost of selling them. For example, making cabinets involves material, labor, and overhead costs, which are part of COGM. When sold, these costs move to COGS. This is important for accurate financial records and pricing.
Why These Differences Matter for Building Materials Businesses
For building materials businesses, knowing the difference between COGM and related terms is key. These businesses often have high labor costs, which make up most expenses. Here’s a breakdown:
Cost Category | |
|---|---|
Initial Building Costs | 2% |
Operations and Maintenance Costs | 6% |
Personnel Costs | 92% |
Focusing on COGM helps find ways to cut costs, like improving labor or operations. This keeps you competitive in a market with small profit margins. Understanding COGS helps price products to cover costs and earn profit.
Important costs like materials and labor should always come first. These costs affect business decisions and resource use. For example, tracking COGM can show production problems. Analyzing COGS can reveal sales trends. Together, these numbers give a full view of your business finances.
How Technology Makes COGM Easier
Technology helps calculate COGM faster and with fewer mistakes. It saves time and gives clearer details about production costs. Tools like ERP systems, cloud software, and Yansourcing make the process simpler.
How ERP Systems Help Automate COGM
ERP systems are very useful for manufacturers. They handle tasks automatically, so you don’t need to enter data by hand. This reduces errors and speeds up calculations. ERP systems also combine data from different areas, making it easier to track costs and share updates.
Here’s what ERP systems can do:
Track costs and manage inventory automatically.
Show real-time data for smarter decisions.
Quickly adjust to changes in production.
Here’s how businesses benefited from ERP systems:
Business Type | Problem | Solution Used | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
Gas Regulator Manufacturer | Trouble tracking finished goods costs | ABC costing, stock tracking by location | |
Fasteners Trading Business | Slow inventory, delayed orders | FIFO system, better purchase planning | Improved stock control by 35%, grew 50% |
ERP systems also include tools like Gantt charts for planning and tracking tasks. These features make managing production costs easier and more effective.
Benefits of Cloud-Based Software for Manufacturing
Cloud software makes COGM calculations even better. You can use it anywhere, which is great for businesses with many locations. It helps cut costs, improve accuracy, and run operations smoothly.
Here are some proven benefits:
Benefit Type | Improvement (%) | Details |
|---|---|---|
Better Operations | Boosted production by using equipment more efficiently. | |
Cost Savings | 31.5% | Lowered costs for labor, materials, and maintenance. |
Labor Efficiency | 43% | Reduced training time with easy-to-use instructions. |
Material Use | 27% | Less waste due to better accuracy in production. |
Energy Savings | 34% | Cut energy costs with smarter systems. |
Maintenance Improvements | 37% | Machines worked better with fewer spare parts needed. |
Faster Production | 39% | Shortened production time with better workflows. |
Scalability | 4.7x | Adjusted production levels more easily. |
Cloud software helps businesses grow, waste less, and expand faster. It’s a great tool for improving COGM calculations.
How Yansourcing Helps with Building Materials
Yansourcing makes managing costs for building materials easier. They help you find good materials at fair prices. They also handle delivery and storage, so you can focus on your work.
Here’s how Yansourcing supports businesses:
Service | What They Do |
|---|---|
They inspect materials to ensure they meet high standards. | |
Delivery Management | They handle storage and make sure materials arrive safely and on time. |
Clear Pricing | No hidden fees, so you know exactly what you’re paying. |
Cost Savings | Avoid common problems and save both time and money. |
Tracking | They monitor every step and keep you updated throughout the process. |
By working with Yansourcing, you can lower costs, improve efficiency, and get top-quality materials. Their services make managing COGM simpler and more dependable.
Conclusion
Now you understand how to figure out COGM and why it matters. By using the steps in this guide, you can calculate COGM correctly and manage production costs better. This helps with inventory control, cutting waste, and working more efficiently. Knowing your total manufacturing cost can make a big difference for your business.
Here’s a summary of the benefits businesses have seen:
Benefit | Percentage Improvement |
|---|---|
Lower inventory costs | |
Higher productivity | 20-40% |
Shorter production times | 30-60% |
Fewer product defects | 20-40% |
Lower overall manufacturing costs | 10-30% |
Start using these ideas now to improve your business in 2025. Tools like ERP systems and Yansourcing can make the process easier and help you focus on growing your company.
FAQ
1. What is the difference between COGM and COGS?
COGM shows how much it costs to make products. COGS tells you the cost of items sold in a set time. Think of COGM as making costs and COGS as selling costs. Both help you understand profits.
Tip: Use COGM to lower production costs and COGS to price items well.
2. How does tracking WIP inventory improve accuracy?
Tracking WIP inventory makes sure only finished goods are counted. This stops mistakes like counting too much or too little. It also helps find problems in production and use resources wisely.
💡 Pro Tip: Update WIP inventory often to keep reports correct.
3. Can technology really simplify COGM calculations?
Yes! Tools like ERP systems and cloud software do the work for you. They track costs, enter data, and give live updates. This saves time, reduces mistakes, and helps you focus on improving production.
Benefit | Improvement |
|---|---|
Time Saved | 80% |
Cost Accuracy | 95% |
4. Why is COGM important for building materials businesses?
COGM helps control spending, manage stock, and set good prices. For building materials, where profits are small, knowing COGM keeps you competitive and avoids wasting money on labor or supplies.
Note: Watching COGM can show where to save money and work better.
5. How can Yansourcing help with COGM?
Yansourcing makes getting building materials easier. They check quality, get fair prices, and handle delivery. This lowers costs and makes it simpler to calculate COGM.
Learn More: Visit Yansourcing’s Building Materials Page for custom solutions.

